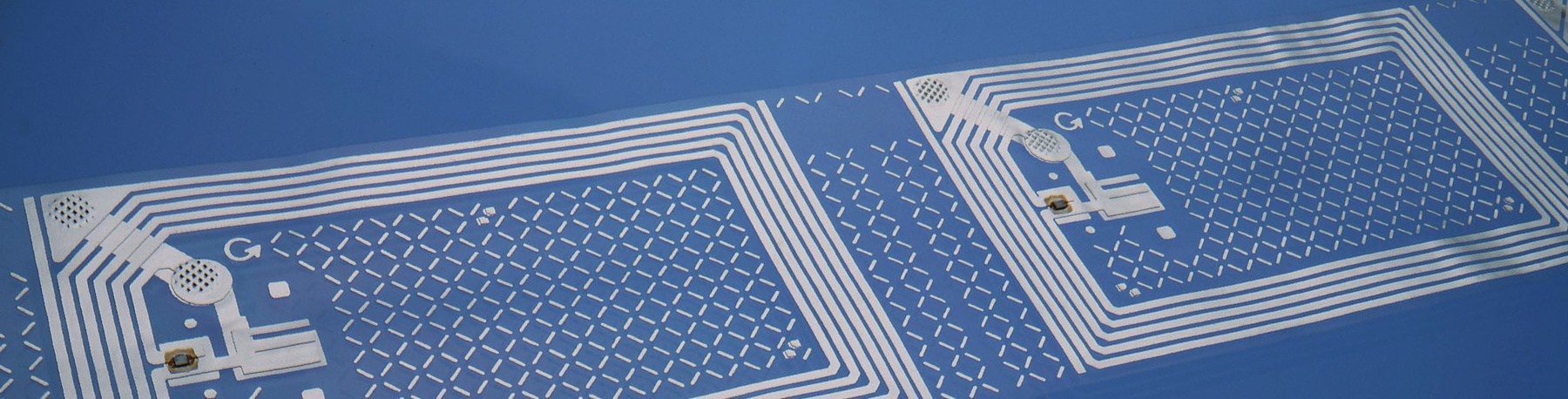
Did you know that 72% of retailers plan to upgrade their supply chain with real-time visibility enabled by automation, sensors and analytics? And, 70% of these retailers are planning to provide item-level RFID tracking technology.Additionally, the International Air Transport Association (IATA) shared results of a study finding that RFID can reduce the number of mishandled bags globally up to 25 percent by 2022.
Delta Airlines, for example, is already using RFID technology at 84 airports. So, what does this mean for future of material handling at parcel & distribution centers, as well as airports?
Evolution of RFID Applications in Material Handling
 For years, airports and supply chain managers have been deploying RFID technology as a tool for real-time tracking and to improve operational efficiency. Beginning its journey in the 1970s, RFID applications took off and by 2014, $9.2 billion was spent on RFID systems.
For years, airports and supply chain managers have been deploying RFID technology as a tool for real-time tracking and to improve operational efficiency. Beginning its journey in the 1970s, RFID applications took off and by 2014, $9.2 billion was spent on RFID systems. Industry experts project growth to more than triple within the next decade. The growing popularity of RFID technology shows a increasing demand toward visibility and accuracy within supply chains.
From initial sorting to final delivery, airports and distribution centers have a unique opportunity to generate insightful and actionable throughput data by leveraging pre-tagged products, parcels and baggage. While current systems may simply record an item moving from point A to point B, RFID takes data a big step by providing more operational data to increase throughput, reduce loss and enhance customer satisfaction.
The Problem: Metallic Interference & RFID Readability
Large amo unts of metal in close proximity to an RFID antennae array causes eddy currents which can amplify or scatter radio waves, thereby compromising the RFID readability and make it difficult to accurately identify individual items. Sometimes, these eddy currents can create their own magnetic field, thereby canceling the reader field altogether.
unts of metal in close proximity to an RFID antennae array causes eddy currents which can amplify or scatter radio waves, thereby compromising the RFID readability and make it difficult to accurately identify individual items. Sometimes, these eddy currents can create their own magnetic field, thereby canceling the reader field altogether.As a result, metal-free zones may be required on the conveyor in close proximity to the RFID reader to enhance read-rates on the RFID tags. Non-metallic materials used in these conveyor sections must meet stringent attenuation and reflectivity requirements to minimize or eliminate false (or null) readings. These non-metallic materials must be thoroughly tested and approved before deployment since the chemical and physical properties of the conveyor section may affect the functionality and performance of the RFID system or even the conveyor itself.
Is there a Required Length for Non-Metallic Sections?
Generally speaking, the accuracy of the RFID system will be enhanced if longer sections of non-metallic conveyor are used. However, non-metallic sections as short as 20” (51 cm) have been shown to be adequate in certain applications. The proper length for a non-metallic conveyor section is generally a function of:- Line-speed
- Signal/antennae strength and ability to adjust/focus antennae read zone
- Item singulation and read-rate accuracy requirements
- Proximity and power level of adjacent RFID reader stations
- Other environmental considerations (i.e., placement limitations)
Extensive lab and field testing have demonstrated that optimal read rates are generally obtained when the minimum length for non-metallic conveyor sections is four feet (1.22 meters). At this length, reflections and tag “de-tuning” will not significantly degrade system performance. Increasing the bed length allows for more robust system performance, particularly in environments with:
- Extreme interference issues
- High sorter speeds
- Applications requiring Read-Write-Verify zones
Are There Alternatives To Non-Metallic Conveyors?
Some integrators and conveyor manufacturers “carve-out” bottom sections of existing metallic conveyors and replace them with commercially available plastic materials such as UHMWPE, creating a “hybrid” configuration. Others have even placed the RFID antennae between the belt and slider-bed surface.Although hybrid configurations may provide minimally sufficient RF coverage in limited applications, hybrid conveyors generally fail to attain comparable read rates over non-metallic conveyor sections and may even be potentially unsafe for item handlers.
Surrounding metallic components in hybrid systems, such as metal cross members or side frames causes RFID interference and RF reflectivity which degrades system performance. Additionally, reflected energy can produce uneven RF fields that can be severe enough to produce “null” spots, or dead zones. This results in insufficient energy directed upon the chipset, causing the tag to be unread.
Also, significant static electricity may built-up with hybrid sections using UHMWPE (or similar material) which is caused by the friction of the conveyor belt across the plastic section. As a result, tags can be destroyed or de-tuned when it comes into contact with this hybrid section, or emit a potentially hazardous electric shock when an individual comes in contact with the conveyor section.
The Solution: Globe Non-Metallic Conveyor Sections
 Globe is the leading manufacturer of non-metallic conveyors and components designed to dramatically improve RFID system performance for manufacturing, parcel, distribution, airport and industrial applications. Globe is the only manufacturer of patented non-metallic conveyor sections (US Patent No. 6,581,759) specifically designed for RFID use. All Globe conveyors a
Globe is the leading manufacturer of non-metallic conveyors and components designed to dramatically improve RFID system performance for manufacturing, parcel, distribution, airport and industrial applications. Globe is the only manufacturer of patented non-metallic conveyor sections (US Patent No. 6,581,759) specifically designed for RFID use. All Globe conveyors a
re manufactured using Brandonite® high-performance polymers. These composite materials are ideally suited for RFID systems because of its superior performance for strength, durability, non-conductivity, signal attenuation, and reflectivity.
Globe non-metallic slider bed conveyors come in lengths from 20" (.51 meters) to 10 feet (3.05 meters) and widths up to 39" (1 meter).
Additionally, Globe manufactures RFID-friendly products to enhance the performance of RFID-enabled systems. It recently introduced the Tuff Tote™ Composite Tray, a 100% non-metallic composite tray that is virtually indestructible and made with Brandonite® composite materials. This resilient and lightweight tote is transparent to RF waves, making it the perfect choice for transporting materials within a factory or distribution centers.
With over a decade of proven success, this engineered composite solution has helped distribution centers to:
Globe non-metallic slider bed conveyors come in lengths from 20" (.51 meters) to 10 feet (3.05 meters) and widths up to 39" (1 meter).
Additionally, Globe manufactures RFID-friendly products to enhance the performance of RFID-enabled systems. It recently introduced the Tuff Tote™ Composite Tray, a 100% non-metallic composite tray that is virtually indestructible and made with Brandonite® composite materials. This resilient and lightweight tote is transparent to RF waves, making it the perfect choice for transporting materials within a factory or distribution centers.
With over a decade of proven success, this engineered composite solution has helped distribution centers to:
 |
Increase Read-Rate Accuracy:Plagued by misreads and double-counts? Globe's Brandonite® polymers offers superior attenuation and reflectivity that enables RFID antennae to accurately read and discriminate chips on even the fastest conveyor systems. Since Brandonite® is virtually transparent to UHF, 5 GHz, 125 KHz, and 13.5 MHz frequencies, you can reduce power settings while eliminating back scatter and overlapping signals. |
|
.png?width=64&height=64&name=mercury-thermometer-and-a-snowflake%20(2).png) |
Withstand Tough Operating Conditions:From -40ºF to +165ºF, our conveyors have been proven to operate without fault in the harshest environments. The use of a self-lubricating, low friction slider bed boosts the lifespan of your belt and drastically reduces energy consumption. |
|
 |
Reduce Energy Consumption:The use of a self-lubricating, low friction slider bed boosts the lifespan of your belt and drastically reduces energy consumption.Globe's Brandonite® materials are virtually transparent to UHF, 5 GHz, 125 KHz, and 13.5 MHz frequencies. This allows you to not only reduce power settings, but also eliminate back scatter and overlapping signals. |
Have a special design requirement or application? We can custom fabricate non-metallic conveyor sections to meet your specific RFID and/or material handling requirement. Interested in learning more about our Patented Non-Metallic Conveyor Systems? Schedule a consultation to discuss your current RFID applications.